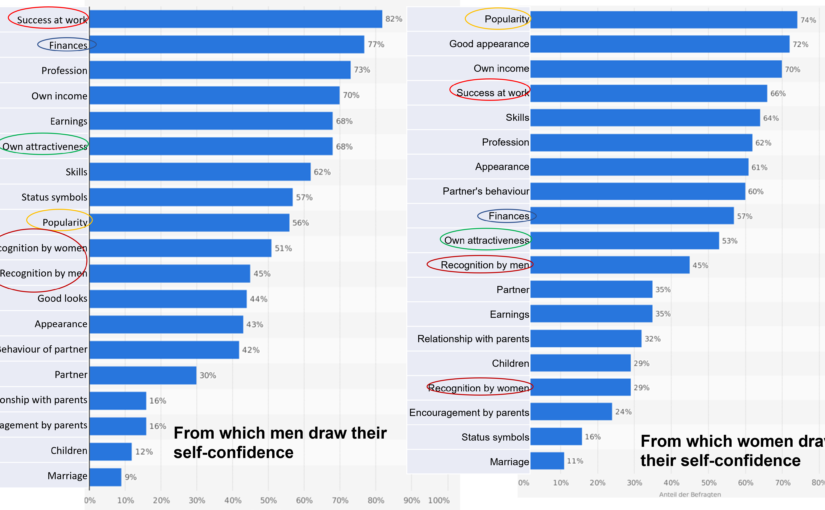
n communication, it is a challenge to be seen and recognized as a partner. Conversations at eye level /as peers are a challenge, when different ways of thinking meet. Flexible thinking would be helpful in such moments. This requires a different attitude as well as a different level of consciousness than exists mainly in the Western world.
Clare C. Graves, evidenced by Don Beck and Chris Cowan, has found different levels of consciousness, which she distinguishes into eight different levels of existence with different patterns of thinking. These thought patterns are based on the motives that drive them. She called this Spiral Dynamics.
Most people in the Western world belong to the first levels / graves (Graves, C. W. (1974). Human Nature Prepares for a Momentous Leap. The Futurist, 72-87.). What they have in common is an egocentric attitude.
The levels of existence, also called Spiral Dynamics. The eight levels / graves are colour coded. They are referred to as WMem. WMem is defined as follows: „A WMem is expressed in a world-view, a value system, a psychological level of existence, a belief structure, an organizational principle, a way of thinking and living“ (Beck and Cowan, 2008, p. 64).
In addition, authors Don Edward Beck and Christopher C. Cowan distinguish between first and second Tier thinking. People with a first Tier mindset usually behave in an ego-driven manner with the main question in mind: „What is the benefit for me? What’s in it for me?“ The first Tier includes five different graves of consciousness with the colours beige, purple, red, blue and orange.
The basic motifs and world-view of the first Tier are:
– Physiological stability (beige),
– Security (purple),
– Domination and power (red),
– Sense and order (blue),
– Autonomy and manipulation (orange),
– Equality and community (green)
The second Tier includes two different graves of consciousness. The second Tier world-view enables the person to respond flexibly to change, to take interconnected, comprehensive perspectives, and to recognize the dynamics of the whole earth, enabling macro-level action. This mindset is consistent with ecosystem and empathic relationship. People with the second Tier mindset tend to behave in an eco-oriented way, asking the most important questions, The questions in their mind are: „What is the benefit of the system in which I am involved? What is the bigger picture and impact on the earth / my environment?“ This second Tier includes two different consciousnesses with the colours yellow and turquoise.
The basic motifs and world-views of the second Tier are:
– Flexibility and natural flow (yellow),
– Life and harmony (turquoise)
Most people are mixed types with different degrees of expression of the first or second level.
The transition from the first to the second level is crucial for the transition from ego-system to eco-system, which is necessary in the VUCA world (Voluntil, Uncertain, Complex, Ambigue) and to evolve to a „Learning Organisation“.
Because of the attitude and mindset of flexibility and harmony, there are no biases, prejudices, or other hierarchical challenges to overcome. The focus is on solving a problem together and developing a process, not on who gets the credit.