To become a true learning organization, it is important to give employees the opportunity to contribute their knowledge and share it within the organization. To do this, the current leadership style should be looked at critically.
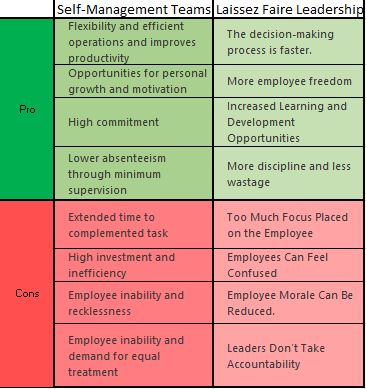
Two leadership principles are readily applied in the VUCA world (volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity). These are the laisse faire and the self-management-team leadership style (see speadsheet). These two styles are very close and have many positive aspects, but they can create confusion and force micropolitical behavior.
Micropolitics: employees strive to increase their own power/influence in the organization in their own interest. This leads to informal rules of the game, social structures that can lead to informal power, and change behaviors in organizations.
My favorite model for leadership that fits best to the VUCA world is the systemic approach SANTIAGO (an acronym) by Prof. Dr. phil. Dr. h.c. Rolf Arnold. The basis of the leadership style is dialogic leadership with a humanistic, subject-oriented and systemic mindset. The attitude of the leaders is not to think they know or can do everything, but to develop solutions with the employees.
To lead in this way, eight principles are important:
- Surrogant (deputy) leadership: employees are trusted to lead themselves. Leadership is a dialogue in which individual human resources are developed. In this approach, leaders are more facilitators and motivators.
- Autopoiesis: this means that human beings are self-sustaining and self-organized. Leaders bring employees out of their own „autopilot“ by questioning, via further development. This moving out of the comfort zone must be accompanied and moderated.
- Never short-term (sustainability): through this approach, managers focus on the development of employees. This leads to medium and long-term effects on the organization and overall development.
- Transformation of interpretive patterns: Leaders in this approach understand their employees‘ interpretive thinking patterns that we have all built from our past experiences. Leaders guide employees to break and change these patterns and transform them into more appropriate interpretations, which means development for the employee.
- Interpretation: interpretation is individual and based on each person’s past. The leader must ensure that the different interpretations lead to successful cooperation and promote the development of the organization.
- Arrangement: In this approach, the leader creates a two-way teaching and learning environment (leader <=> staff). Employees are empowered, motivated and take responsibility for their development and business results. The basis for this kind of leadership is trust and regular dialogue, as well as an open-minded curiosity for the individual.
- Go with serenity: The leader needs a lot of serenity with this approach, because the acceptance and implementation of this leadership approach takes time and contradicts the learned patterns of traditional leadership. It is necessary to break through the patterns of interpretation.
- Organizational learning: Through staff development, the organization can learn. Organizational learning happens through the employees as part of the organization. The organization influences the employees, but it also works in the other direction. The behavior of the individual employee influences the organization.
To make sure that you are as a leader on the right way, ask your team anonymously, if these elements are lived by you. Have you every tried to get honest feedback from your employees regarding your leadership style?


